From session replay to development plan: annotations in full stack session recordings
Add sketches, notes, and requirements directly to your full stack session recordings. Highlight interactions, API calls, or traces and turn them into actionable development plans or AI prompts.
Traditional session replay tools give you a window into what the user saw.
A few let you blur sensitive data or leave a quick sketch. Some rely on third-party integrations to manage annotations. Most just let you add comments to the overall recording.
What they don’t give you is a way to connect annotations to the actual system data: the API calls, traces, and logs that explain what really happened. And they certainly don’t make those annotations AI-ready, so you can feed them straight into your IDE or coding assistant.
That’s where Multiplayer annotations come in.
Practical use cases
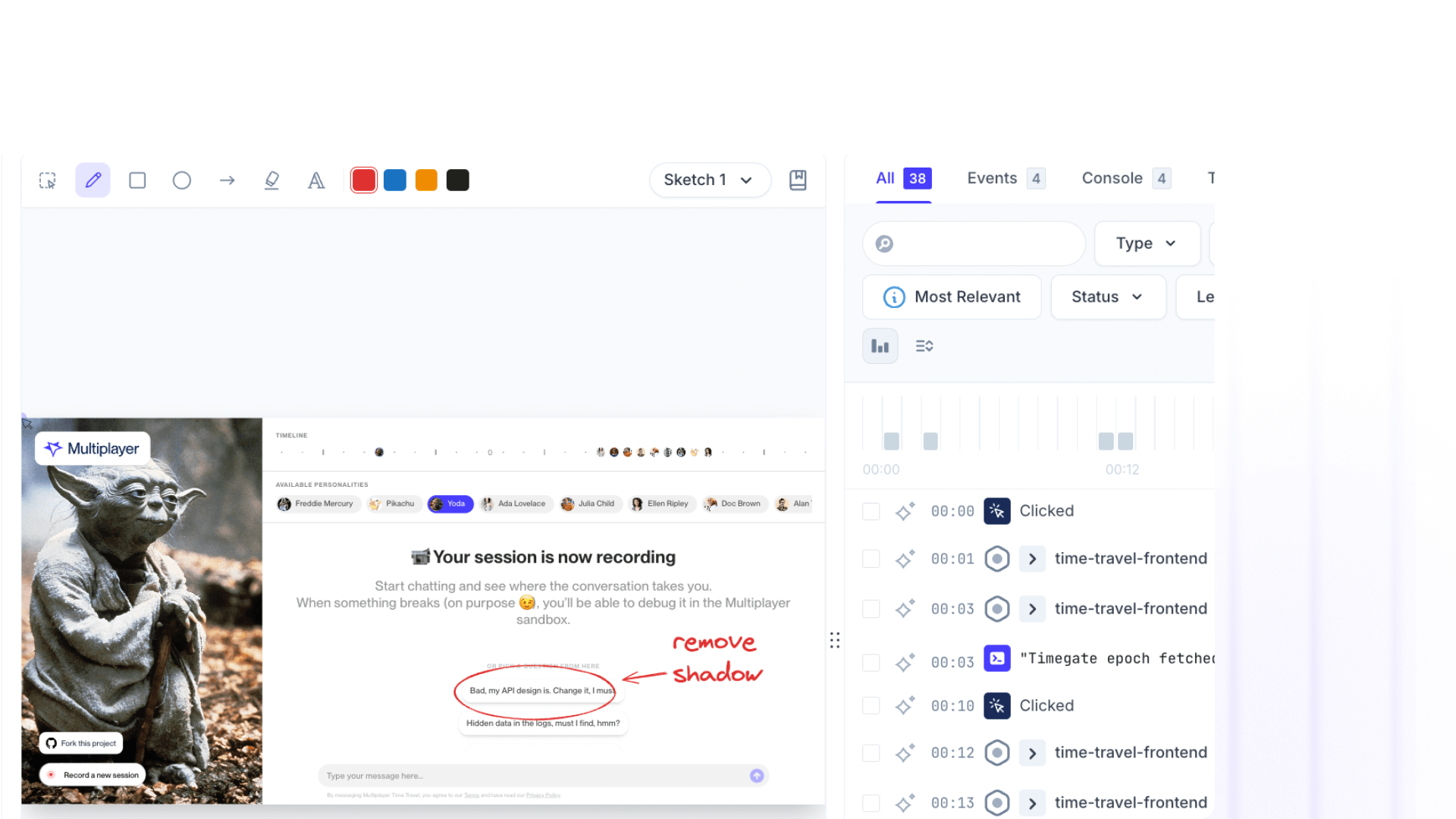
Notes in Multiplayer transform raw session recordings into executable development plans. Whether you're debugging a technical issue, clarifying requirements, planning a refactor, or designing a new feature, notes capture your thinking directly on the timeline, attached to the exact moments, interactions, and backend events that matter.
Instead of writing requirements in a vacuum or describing bugs in abstract terms, you're annotating actual behavior with full-stack context automatically included.
(1) From Replay to Plan
This is how a traditional workflow might look like:
- Watch a session recording of the user actions (only frontend data)
- Switch to a separate tool (Jira, Linear, Notion)
- Try to describe what you saw in text
- Lose technical context in translation
- Respond to all the clarifying questions
- Repeat the cycle
With Multiplayer annotations:
- Watch the full stack session recording
- Sketch directly on problem areas as you see them
- Add timestamp notes explaining what should happen instead
- Annotate the specific API call or trace that needs modification
- Share the annotated recording with your team
The result is precise, contextualized instructions that include:
- Visual markup showing exactly which UI elements need changes
- Timestamp notes explaining the intended behavior at each step
- References to the actual API calls, database queries, and service traces involved
- On-screen text specifying new copy, error messages, or validation rules
- Sketched mockups showing proposed layouts or flows
Engineers receive a complete specification with runtime context.
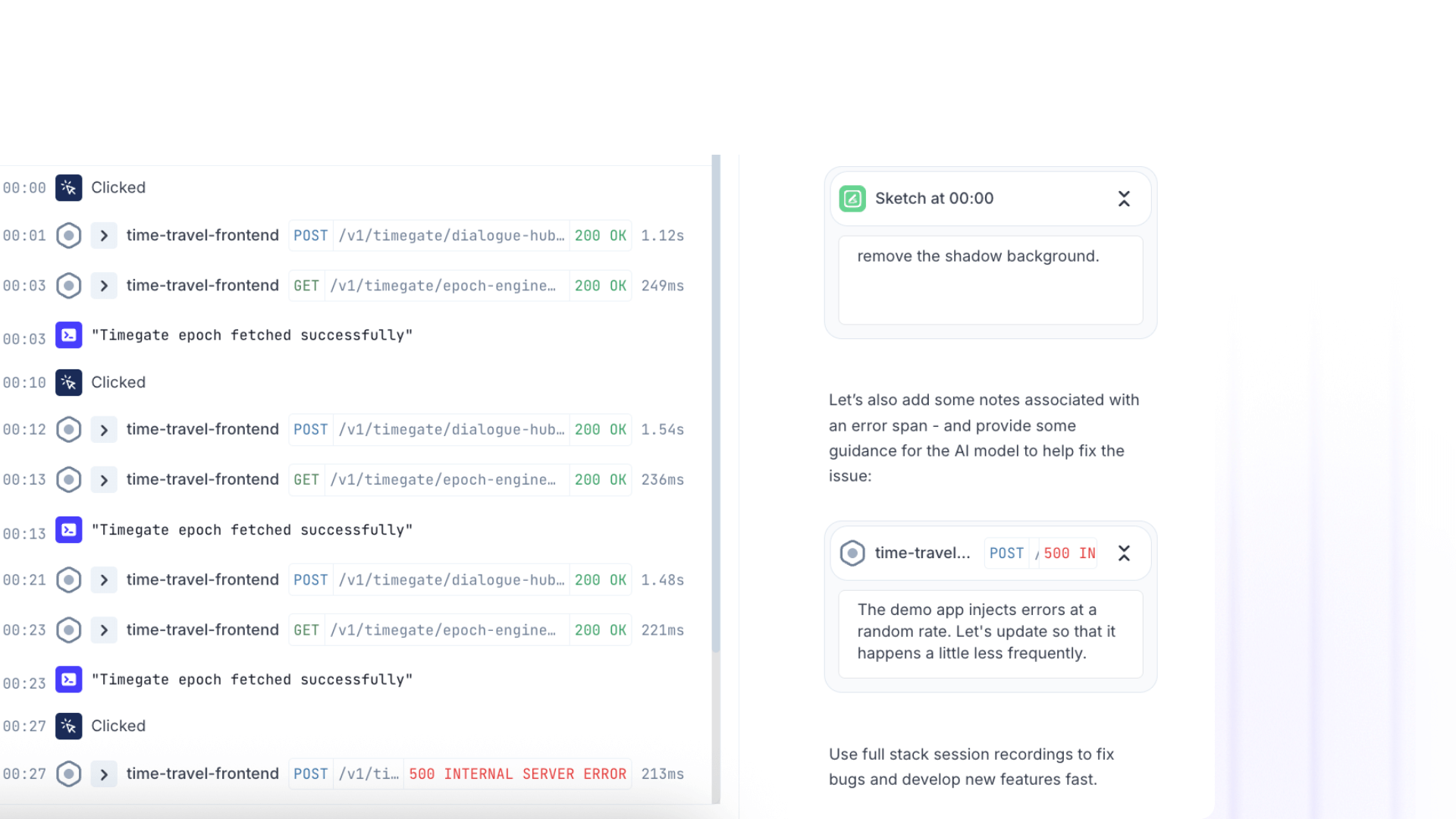
(2) Cross-Role Collaboration
Annotations create a shared visual language that works across teams and disciplines:
Support → Engineering handoffs: Support annotates a customer's session with red circles around the confusing UI, timestamp notes explaining what the customer tried to do, and highlights on the error response that needs better messaging. Engineering sees the bug with full reproduction context in under a minute.
Product → Engineering workflows: PM annotates a user session showing where people drop off, adds sketches proposing a new flow, and attaches notes with acceptance criteria. Engineer reviews the annotated session and knows exactly what to build, with examples of the current behavior and references to the code paths involved.
QA → Development feedback loops: QA records a test run, annotates edge cases with highlights, adds notebooks with each test scenario, and circles areas where behavior differs from specs. Developers receive visual test documentation tied to actual execution traces.
Engineering → Vendor communications: When working with third-party APIs or external teams, engineers can record integration behavior, annotate failing requests with technical details, sketch expected responses, and share the annotated session. Vendors see exactly what's happening in your system without needing access to your codebase.
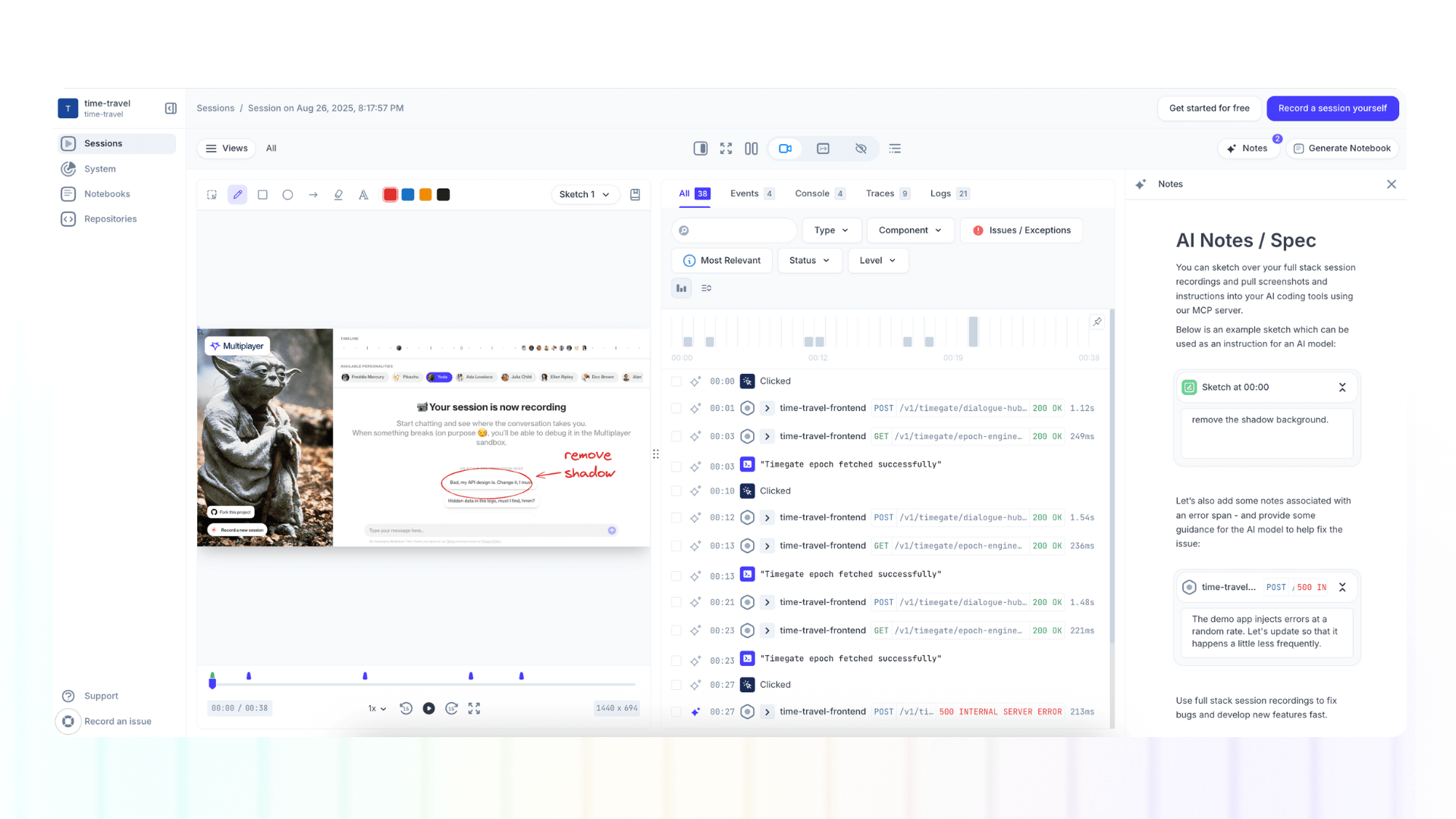
AI-Ready Context
Use the Multiplayer MCP server to pull your full stack session recording screenshots and notes into your AI coding tools.
Because annotations carry metadata, they’re machine-readable. They’re not just helpful for humans, they’re structured context your AI tools can consume directly.
This means your copilot doesn’t just “see” a session: it understands the requirements, context, and team intent tied to that session. From there, it can generate accurate fixes, tests, or even implement new features with minimal prompting.
Traditional AI prompting:
"Add validation to the signup form"AI generates generic validation without knowing your form structure, existing patterns, or backend constraints.
AI prompting with annotated sessions:
Share an annotated Multiplayer recording showing:
- The signup form with red circles around fields needing validation
- Timestamp note: "Email validation should reject addresses without proper domains"
- Highlighted API call showing the current /signup endpoint contract
- Text annotation specifying error message copy
- Trace showing the validation happens client-side only (needs backend validation too)AI now has:
- Visual context of your actual UI
- Specifications for the exact behavior you want
- Technical context of existing API contracts
- Requirements for both frontend and backend changes
- Examples of current behavior vs. desired behavior
👀 If this is the first time you’ve heard about Multiplayer, you may want to see full stack session recordings in action. You can do that in our free sandbox: sandbox.multiplayer.app
If you’re ready to trial Multiplayer you can start a free plan at any time 👇